Understanding earthquakes requires comprehending various aspects, starting with seismic waves, a phenomenon significantly influenced by the location of an earthquake’s origin. The United States Geological Survey (USGS) provides valuable data and resources regarding earthquake occurrences, including information related to depth. Fault lines, geological structures where seismic activity occurs, are crucial in understanding where and how earthquakes initiate. Considering these factors is key to understanding what is focus earthquake and how these events, originating at varying depths beneath the Earth’s surface, can impact our lives. Learning about these factors is essential for safety and preparedness.
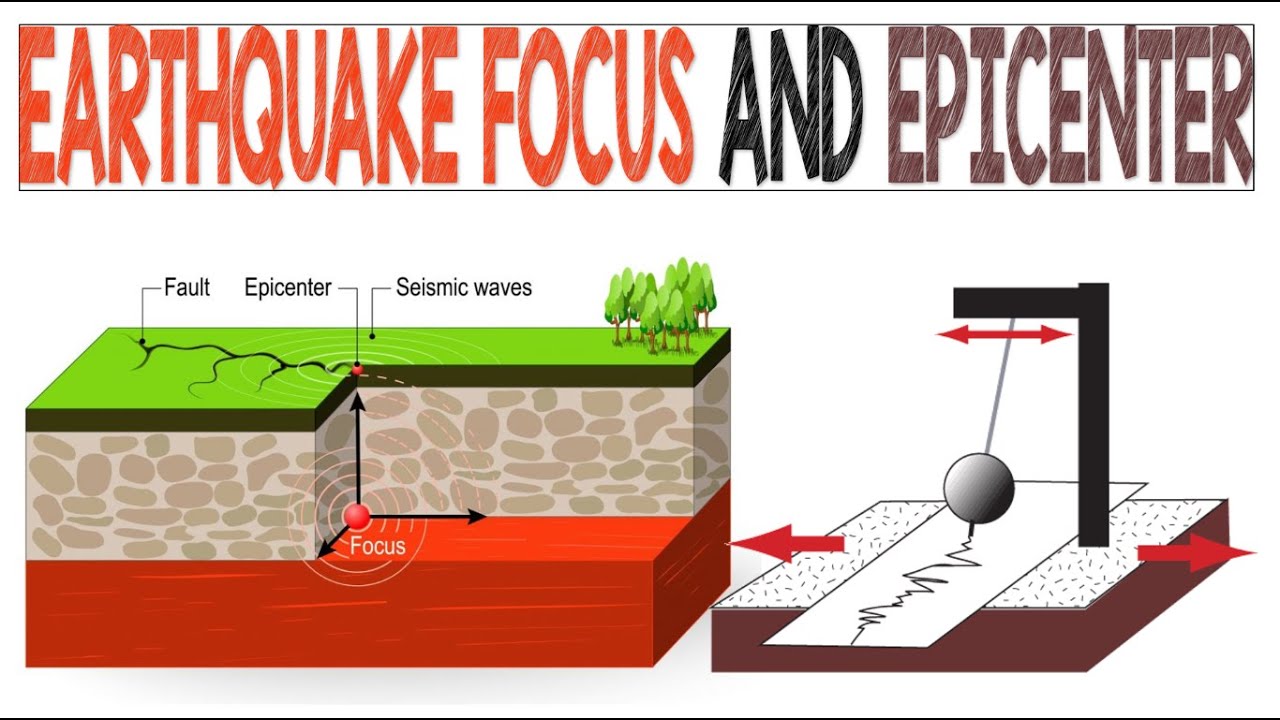
Image taken from the YouTube channel EarthPen , from the video titled Earthquake Focus and Epicenter | Animation .
Understanding Focus Earthquakes: A Guide to Safety
This article aims to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of focus earthquakes, often referred to as hypocenter earthquakes. We will explore what these earthquakes are, where they originate, and crucially, how to stay safe during and after one.
What is a Focus Earthquake? Delving into the Hypocenter
The term "focus earthquake" centers around understanding the hypocenter. The hypocenter is the point of origin of an earthquake within the Earth. This is where the rupture begins, releasing seismic waves that radiate outwards. Understanding the location of the hypocenter is crucial to understanding the earthquake’s potential impact.
Defining the Hypocenter
The hypocenter is essentially the "epicenter’s source." While the epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter, the hypocenter is the actual point of rupture underground. Think of it like this:
- Epicenter: Where the earthquake is felt strongest on the surface.
- Hypocenter: Where the earthquake started deep within the Earth.
Why the Hypocenter Matters
The depth of the hypocenter significantly influences the intensity of shaking felt at the surface. Generally:
- Shallower hypocenters (closer to the surface) tend to cause more intense shaking locally. The energy has less distance to dissipate.
- Deeper hypocenters (further from the surface) may affect a broader area, but the intensity of shaking at any single location might be less.
Key Differences: Focus (Hypocenter) vs. Epicenter
It’s important to distinguish between the focus (hypocenter) and the epicenter. The following table highlights their key differences:
| Feature | Hypocenter (Focus) | Epicenter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Point of origin within the Earth | Point on the surface above the hypocenter |
| Location | Underground | Surface of the Earth |
| Significance | Where the earthquake begins | Where the earthquake is usually first reported |
Factors Affecting Earthquake Intensity
Several factors beyond just the depth of the hypocenter contribute to the intensity of an earthquake at the surface:
- Magnitude: The amount of energy released during the earthquake. Measured using scales like the Richter scale or the Moment Magnitude scale.
- Distance from the Epicenter: The closer you are to the epicenter, the stronger the shaking you’re likely to experience.
- Local Geology: Soil type and underlying rock formations can amplify or dampen seismic waves. Soft soils, for example, tend to amplify shaking.
- Building Construction: The design and materials used in buildings significantly affect their vulnerability to earthquake damage. Buildings designed to withstand seismic forces are much safer.
Staying Safe During and After an Earthquake
Preparation and knowledge are essential for staying safe during and after an earthquake.
Before an Earthquake
- Secure Your Home: Bolt heavy furniture to walls, move heavy objects to lower shelves, and secure hanging objects.
- Create an Emergency Kit: Include water, non-perishable food, a first-aid kit, a flashlight, a whistle, a battery-powered radio, and any necessary medications.
- Develop a Family Emergency Plan: Discuss evacuation routes, meeting points, and communication strategies. Practice earthquake drills regularly.
- Know Your Surroundings: Identify safe spots in your home, workplace, and other frequently visited locations.
During an Earthquake
- "Drop, Cover, and Hold On": This is the recommended action. Drop to your knees, cover your head and neck with your arms, and hold onto something sturdy.
- If Indoors: Stay inside. Move away from windows, mirrors, and anything that could fall.
- If Outdoors: Move to an open area away from buildings, trees, power lines, and anything else that could fall.
- If in a Vehicle: Pull over to a safe location away from overpasses, bridges, and power lines. Stay in the vehicle until the shaking stops.
After an Earthquake
- Check for Injuries: Assist anyone who needs help.
- Be Prepared for Aftershocks: These smaller earthquakes can occur after the main shock and can cause further damage.
- Inspect Your Home for Damage: Check for gas leaks, structural damage, and other hazards. If you suspect a gas leak, evacuate immediately and report it to the authorities.
- Listen to the Radio or Television for Emergency Information: Follow instructions from emergency officials.
- Avoid Damaged Areas: Stay away from areas where buildings or infrastructure have been damaged.
- Conserve Resources: Water, food, and other supplies may be limited. Use them sparingly.
By understanding "what is focus earthquake" and being prepared, you can significantly improve your safety and the safety of those around you during and after a seismic event.
Focus Earthquakes: FAQs for Enhanced Understanding
Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand focus earthquakes and how to stay safe.
What exactly is a focus earthquake?
A focus earthquake, also known as a deep-focus earthquake, is an earthquake that originates at a significant depth within the Earth’s mantle. The "focus" refers to the point of origin of the earthquake rupture underground. Unlike shallow earthquakes, these occur much deeper, typically between 300 and 700 kilometers below the surface.
Are focus earthquakes more or less dangerous than shallow earthquakes?
Generally, focus earthquakes are less dangerous than shallow earthquakes of the same magnitude. The energy released has to travel further to the surface, which dissipates some of the intensity. However, a very large magnitude focus earthquake can still cause significant damage over a wide area.
Why do focus earthquakes happen so deep within the Earth?
The exact mechanisms behind deep-focus earthquakes are still not fully understood. Scientists believe they may be related to mineral phase transitions – changes in the crystal structure of minerals under extreme pressure and temperature deep within the Earth.
What should I do differently during a focus earthquake compared to a shallow earthquake?
The basic safety guidelines remain the same: Drop, Cover, and Hold On. However, because focus earthquakes often affect a larger area, being aware of potential hazards in your wider region is important. Stay informed about earthquake risks in your area through local authorities and emergency management agencies.
So, there you have it – hopefully you have a better idea of what is focus earthquake now! Stay safe out there, and always be prepared. We appreciate you stopping by!